HOW DYNAMIC BALANCING RESOLVES UNBALANCE FAULT IN ROTATING PARTS
Firstly, unbalance-related issues are common causes of vibration in industrial fans, impellers, and other rotating parts of equipment.
Therefore, unbalance occurs when a rotating part’s center of mass or its inertia axis, is no longer aligned with the part’s center of rotation or its geometric axis. This fault causes an unsteady movement of rotating parts from side to side.
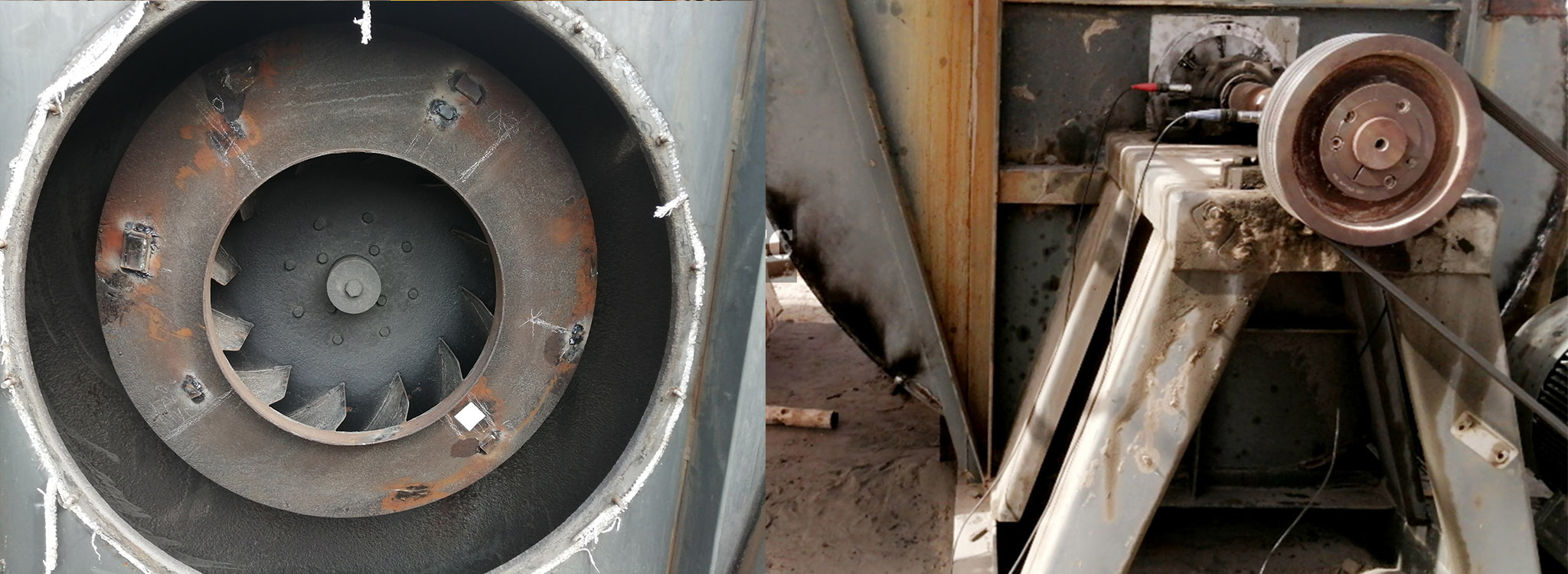

Above all dynamic balancing is a procedure whereby rotating parts are balanced either by addition or removal of mass while the part is in motion. This procedure can either be done on a single plane or two planes.
In addition, we always recommend rotating equipment to balance per the international ISO reference standard for quality balancing. Contact us today.
Schematic Diagram Showing Balancing Results of Rotating Parts
The below images shows vibration and balancing results before and after dynamic balancing services for different rotating equipment
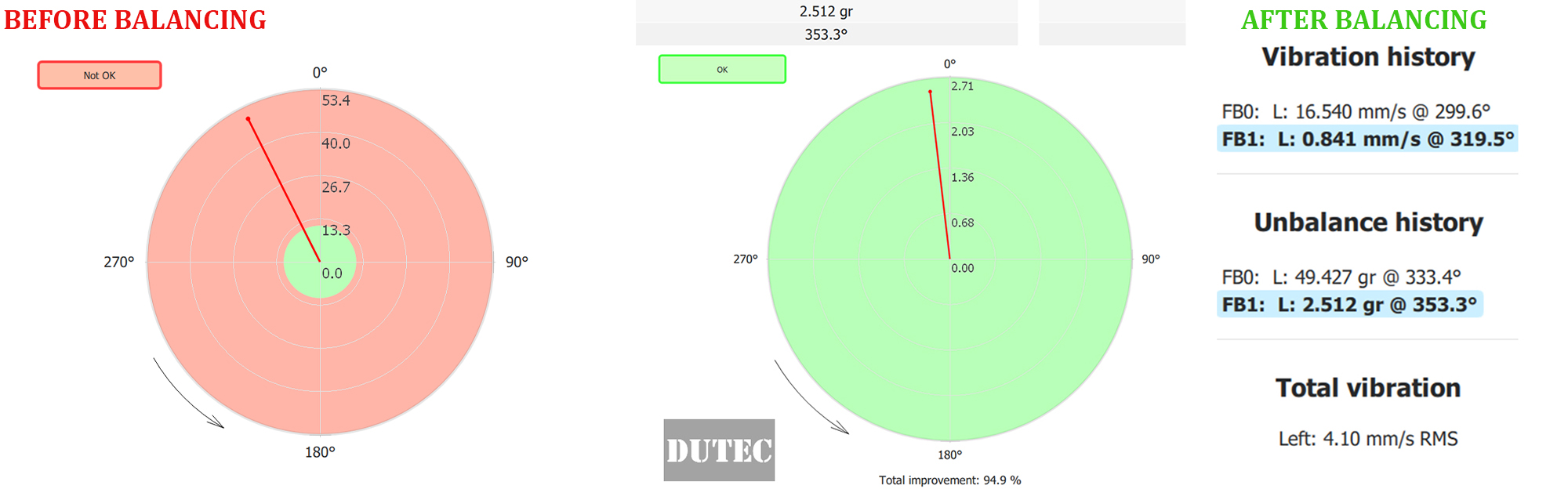
1. balancing of Crusher Fan with motor pump
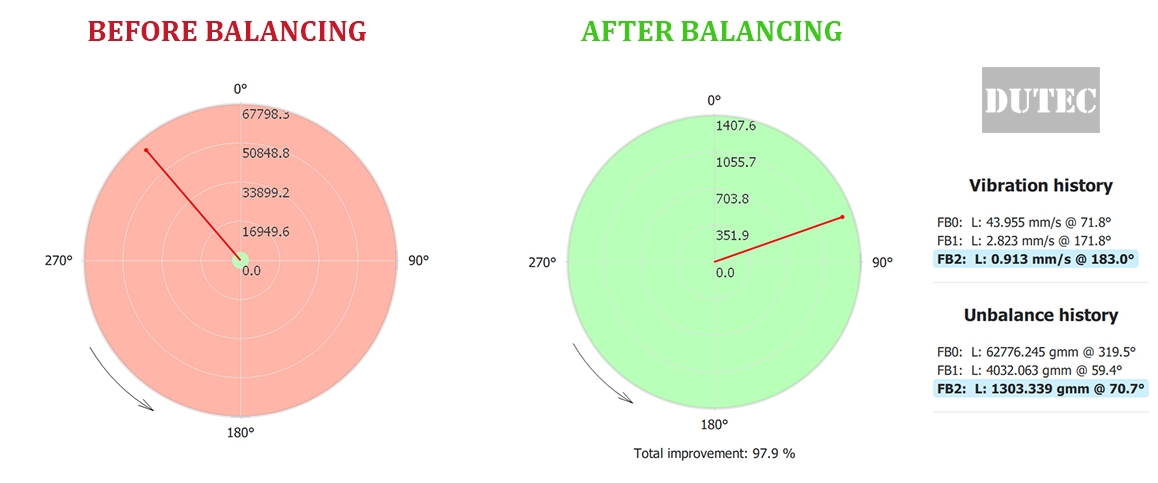
2. balancing of A Flash Dryer
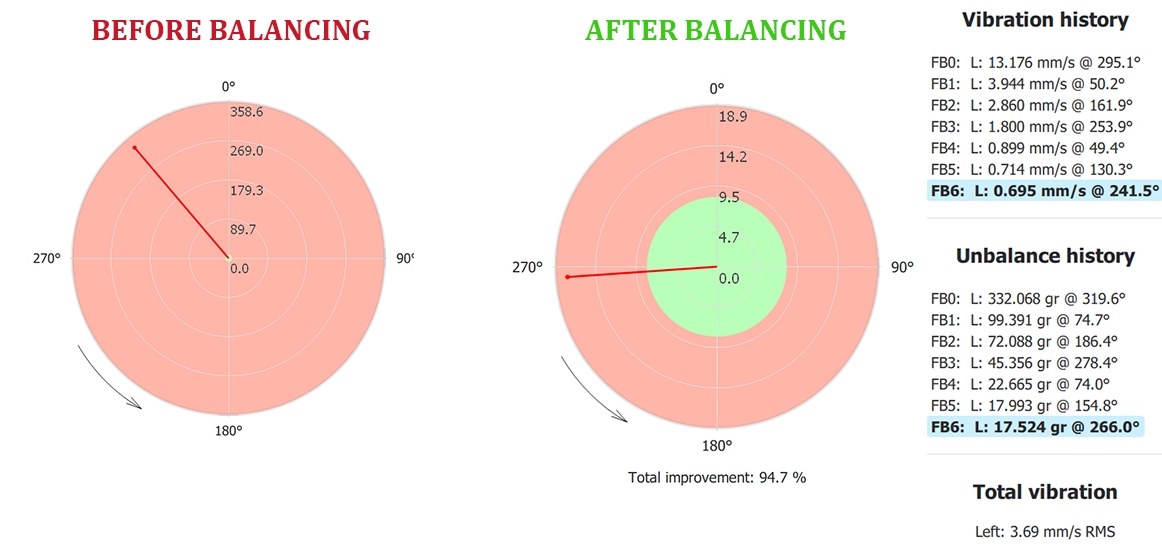
3. balancing of impeller Fan
If you need more information on fan impeller balance, you may be interested in below blogs;
- How Dynamic Balancing Resolves Unbalance Fault in Rotating Parts
- Onsite Dynamic Balancing Services
- How To Balance A Fan Impeller And Blower
- Dynamic Balancing Services of Fan Impellers And Blowers
You can always Contact Us or Request a Quote for more details.